Course Content
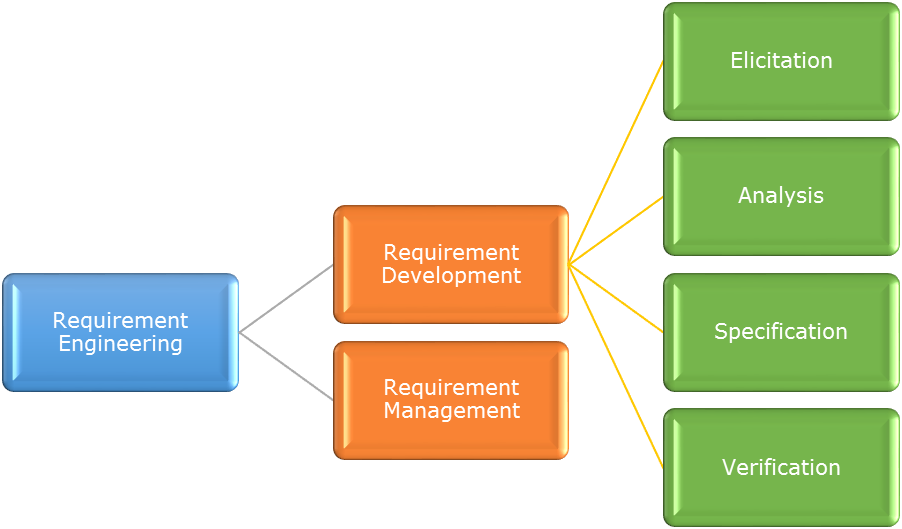
Introduction to Requirement Engineering
- Framework for Requirements Engineering
- Rationale for Requirements Engineering and the problems with requirements
- The Definition and Characteristics of Requirement
- The Characteristics of a Requirements Engineering Process
- The Problems of Defining Requirements
- The Requirements Engineering Framework
- Requirement Engineering Activities
- Importance of Requirements Planning and Estimating
- Business Rationale and Input
- Business Process Analysis Model and Inputs into ‘The Define Requirements’ Stage
- Business Case in Project Life-Cycle
- Terms of Reference/ Project Initiation Document/ Project Charter–business objectives, project objectives, scope, constraints (budget, timescale, standards), sponsor (authority), resources and assumptions
Hierarchy of requirements
- Building the hierarchy through decomposition of requirements
- Categories of requirements within the hierarchy
- General business requirements, including legal and business policy
- Technical policy requirements
- Functional requirements
- Non-functional requirements, that include performance, availability, robustness, usability, robustness, access, security, archiving, backup and recovery
Stakeholders in the requirements process
- The definition of the term ‘stakeholder
- Role and Contribution of Project Stakeholders to the requirements engineering process
- Project Manager
- Business Analysis
- Solution
- Developer
- Testers
- Architects
- Role and contribution of Business Stakeholders to the requirements engineering process
- Project Sponsor
- Subject matter expert
- End users and managers
- Role and Contribution of External stakeholders to the requirements engineering process
- Customers
- Regulators
- Suppliers - products and services
Requirements Elicitation
- Knowledge types –tacit and non-tacit(explicit)
- Elicitation techniques
- Interviews
- Workshops
- Observation
- Formal/informal
- Shadowing
- Focus groups
- Prototyping
- Scenarios
- Document Analysis
- Special purpose records
- Questionnaires
- Activity sampling
- Understanding the applicability of techniques
Use of models in Requirements Engineering
- The purpose of modelling requirements
- Generating questions
- Cross checking for consistency and completeness
- Defining business rules
- Modelling the business context for the system using a context diagram that identifies the inputs and outputs of the system
- Developing a model to represent the system processing requirements .Use case diagrams – actors, boundaries, associations, use cases
- Interpreting a data model based upon the system data requirements Class diagram –classes, simple associations, multiplicities, attributes
Requirement documentation
- Documentation styles and levels of definition
- User Stories
- Use Cases
- Requirements List
- Requirements Catalogue
- Requirements Catalogue
- Identifier
- Name
- Description
- Acceptance criteria
- Source
- Owner
- Rationale/Benefits
- Related non-functional requirements
- Priority
- Type (functional, non-functional, general, technical)
- Related requirements/documents
- Author
- Version control/status
- Change history
- Resolution
- Requirements Document
- Introduction and Background
- Business Process Models
- Function models (use case diagram) of defined requirements
- Data model (class model) of defined requirements
- Requirements catalogue
- Glossary
Requirements Analysis
- Prioritising and packaging requirements for delivery
- Organising requirements
- Requirements filters
- Characteristics of a good requirement
- Removing duplicated requirements
- Reconciling overlapping requirements
- Identifying and negotiating conflicts between requirements
- Removing ambiguity
- Ensuring feasibility(technical, business and financial)
- Ensuring testability
- Ensuring traceability
- Prototyping requirements
- Verifying requirements
Requirements Validation
- Agreeing the requirements document
- Types of reviews
- Informal reviews
- Structured walkthroughs (author-led review)
- Technical reviews
- Inspections
- Stakeholders and their areas of concern
Requirements Management
- Dealing with changing requirements
- The sources of change
- Change Management
- Configuration management
- The importance of traceability
- Vertical traceability (to business objectives)
- Horizontal traceability (from origin to deliver)
- Traceability and ownership
- Requirements Engineering support tools
- CARE Tools (Computer Aided Requirements Engineering)
- CASE Tools (Computer Aided Software Engineering)

 ENQUIRE
ENQUIRE
 REQUEST CALLBACK
REQUEST CALLBACK
 GET A FREE QUOTE
GET A FREE QUOTE


 Introduction
Introduction Course Details
Course Details Course Content
Course Content




 London
London